S and dunes are masses of loose sand that move across the ground in wind. This process causes a sand dune to migrate down wind.
Sand Dune Formation Howstuffworks
The grains are blown up the windward side of a dune until they reach the top.
. Sand is dormant but the forces of wind and water that move geological structures are very much active. Dune systems are formed in areas where there is a broad area of sand either terrestrial or underwater. Eventually sand slides under its own weight and the dune slowly migrates.
The more powerful a wind is the farther it can carry particles of sand before they drop to the ground. Dunes grow as grains of sand accumulate. This continued action moves the dune across the landscape.
With strong long-lasting winds. In regards to sand dunes they migrate in the direction of the wind as sand particles being individually light can travel on the wind in forms of sand storms and therefore migrate overtime. An obstacle for the dune to form against eg.
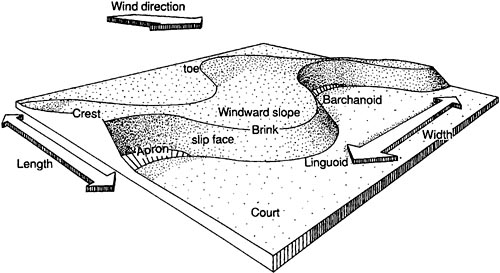
As they roll and bounce on the ground these particles create small wave-shaped ripples of sand. The linear sand dunes require strong winds from two directions for their creation. As such they form in the presence of both the primary wind and cross-wind directions.
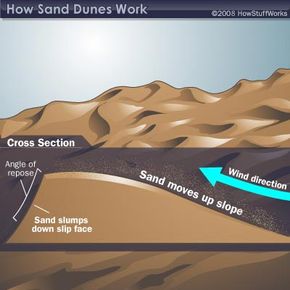
Viewed from one end sand dunes have a flat back side and a steep front side. About 95 percent of sand grains move in this manner. This angle usually about 30-34 is called the angle of repose.
A large flat beach. It is estimated to. Dunes form when wind blows sand into a sheltered area behind an obstacle.
The 30 square mile 78 sq. The wind blows up the back side of the dune. A large supply of sand.
As more sand collects the slope steepens and some of the sand slides down the slip face of the dune. Ridges that slowly move. An onshore wind wind blowing from the sea to the land for sand to be transported to the back of the beach.
Sand dunes are among natures loveliest wonders forming undulating mounds in deserts on beaches and even underwater. The movement of wind and water shifts the sand to create the dunes. These ripples can build up into larger structures called dunes.
Sand is continually eroded from its upwind side and deposited on its downwind side. The traditional Ute word for the Great Sand Dunes is Saa waap maa nachesand that moves Though the locations of the larger dune forms have remained fairly constant for centuries some smaller. Winds may erode a section pushing the sediment leeward.
Wind blows sand into dune shapes that are asymmetrical. They are ever-changing structures. Sand moves up the gentler side of the dune by saltation and accumulates just beyond the crest of the dune.
Then they drop down into the shelter of the lee the side away from the wind. The collapsing sand comes to rest when it reaches just the right steepness to keep the dune stable. Sand accumulates on the leeward side of the dune allowing the slope to steepen.
The animation below gives a basic overview of how they form. Two distinct processes are known to act on dynamic dunes the process of migration by erosion on the windward side and deposition on the lee side typical for transverse dunes and the process of elongation typical for linear dunes. The most common deflation feature is the blowout a bowl-shaped depression with a flat floor that lies below the elevation of most of the adjacent dunes.
Other grains are blown up and over burying the first. Parabolic dunes also called U-shaped blowout or hairpin dunes tend to form where vegetation covers the sand. Furthermore the linear sand dunes possess long.
Time for the sand to dry so an extensive tidal range is needed. As the wind picks up the sand the sand travels but generally only about an inch or two above the ground. Sand dunes are hills of sand that are made by winds as they blow across deserts.
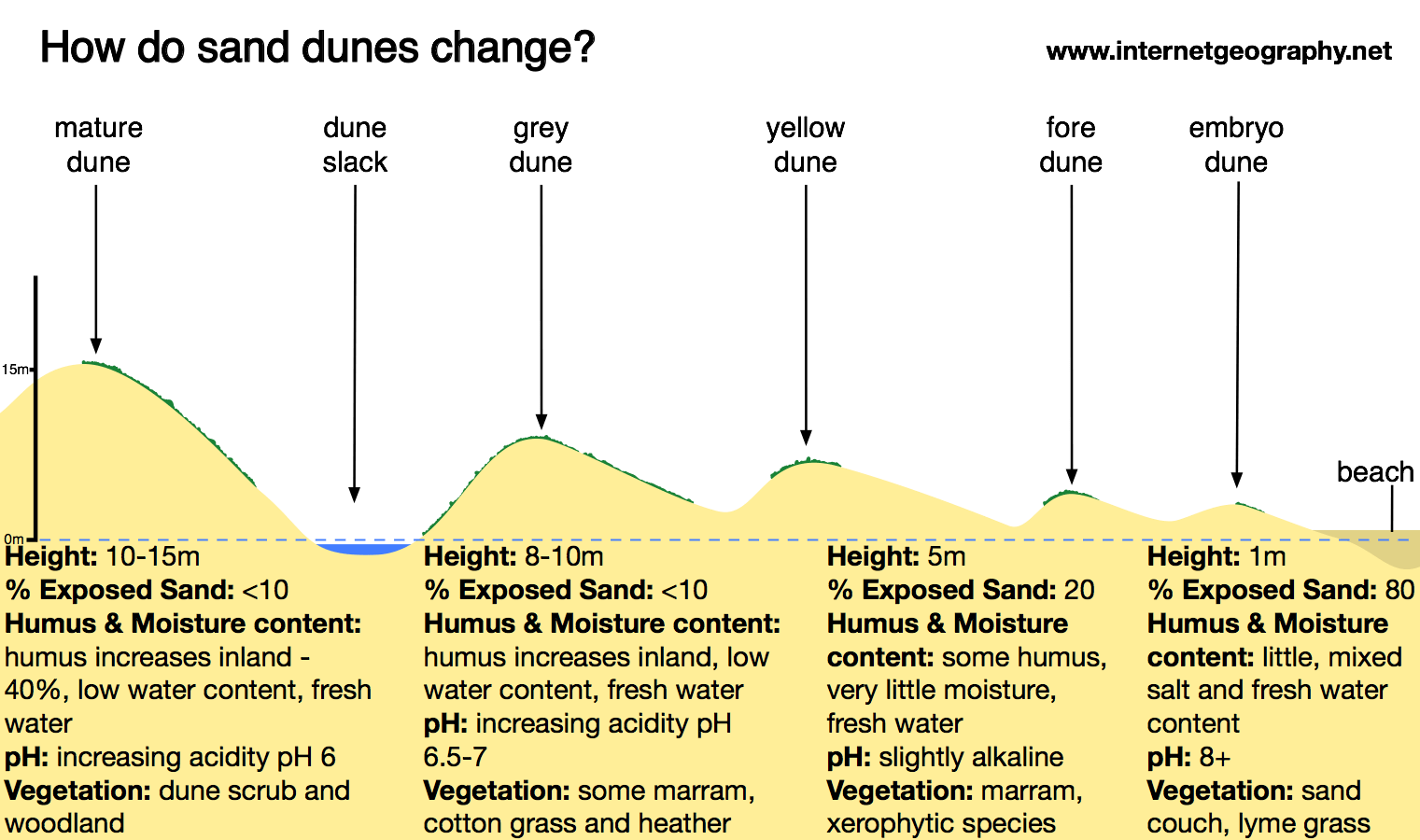
How do sand dunes migrate. Traveling further from the beach towards the back of the dunes the vegetation starts to change. Simply put the linear dunes form in bidirectional wind regimes.
Wind moves sand in one of three ways. Like a game of leapfrog a dune slowly moves as grains of sand move up the windward face and down the leeward slope called a. A sand dune is a hill or ridge beyond the reach of the tides formed from sand over many years.
Every dune has a windward side and a slipface. Blowouts are flat-floored because the sand is blown away until the sand surface. Sand blows up the.
The sand grains bounce along in the wind. The conditions required for sand dune formation are. Where these three variables merge a sand dune forms.
Wind continues to move sand up to the top of the pile until the pile is so steep that it collapses under its own weight. Most of them form in desert places where there is barren ground between the dunes. A dunes slip face is simply the side without wind.
Dunes are also known to migrate and now a new study suggests that they. These two processes are determined by wind direction relative to the dune alignment. Dunes form when wind blows bits of sand into piles creating mounds or.
Once sand begins to pile up ripples and dunes can form. The dunefield is composed of reversing dunes transverse dunes star dunes and a few barchan dunes. Side of a dune and slides down the.
At Great Sand Dunes you can witness geology coming alive. One way in which sand dunes are eroded is by the wind remobilizing sand and blowing it out of the dune a process known as deflation. Dunes usually form in bands parallel to the beach getting taller and more chaotic the further away you get.
It is stabilized by opposing wind directions southwestly and northeasterly creeks that recycle sand back into it and a 7 moisture content below the dry surface. Km active dunefield is where the tallest dunes reside. The vegetation will hold back the arms of the dune so that the dune points in the leeward direction.
A dunes windward side is the side where the wind is blowing and pushing material up.

0 Comments